Further evidence is linking the Zika virus to fetal brain damage and now to serious neurological disease in adults. In the first paper researchers performed brain scans on 23 babies born to mothers thought to be infected with Zika. The scans revealed a majority of the babies had severe brain malformation and scar-like lesions […]
Tag: neurology
Restoring movement to a quadriplegic patient
Researchers have successfully restored some movement to the fingers, hand, and wrist of a quadriplegic patient by using recorded signals from his motor cortex, allowing him to perform daily living activities such as pouring from a bottle and stirring the contents. Systems that work by translating neural activity into signals for robotic devices, such as […]
Stop screening for developmental delay
The Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care recommends against using a screening test to identify developmental delay in young children who show no apparent signs of delayed development. The recommendation applies to children aged one to four years old who have no visible signs, or whose parents have no concerns, of delay. Developmental delay […]
Shared semantic structure between human languages
Human languages share a common semantic structure regardless of the regional environment in which a language evolved, according a study of 81 languages. The authors believe concepts expressed in language may arise from universal properties of human cognition. Examining how words are related to other words in a language revealed a universal semantic network. For […]
Why the brain has its folds
The folds on the surface of the human brain exist because of physics, not biology, according to a new study using 3D printing. The researchers believe their results suggest that physical forces play a crucial role in neurodevelopment, and may provide insights into diagnosing and treating some neurological disorders. The study proves a model from […]
Genetically mapping the cause for schizophrenia’s synaptic loss
Mapping genetic variations has allowed researchers to identify a potential mechanism to explain the onset of schizophrenia. The authors hope this will provide insights into the risk of developing schizophrenia as well as the neurobiology of the disease. Variations in the genetic code controlling the production of C4, a protein known for the role it […]
Studying autism with genetically modified monkeys
Genetically modified monkeys showing autism-like behaviours could help the development of strategies to treat the symptoms of autism disorders, according to researchers. Currently one of the major challenges for researchers studying autism spectrum disorders is the lack of animals models that reproduce symptoms typically found in human patients. These monkeys, and their offspring, show behavioural […]
Language changes brain patterns
Very early language experience will influence how a child’s brain processes a new language later in life, according to a study in Nature. Researchers examined three groups of children, all of whom were fluent in French. One group had no exposure to Mandarin, another was fluent in Mandarin, and the last third group had been […]
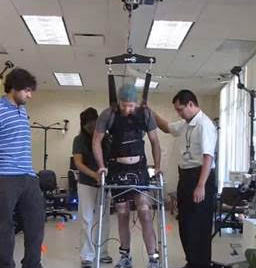
Teaching a paraplegic to walk
For the first time a person with complete paralysis in both legs (paraplegia), arising from a spinal cord injury, was able to walk without relying on manually controlled robotic limbs. The results show that brain-controlled walking can be restored after a complete spinal cord injury. After undergoing mental training, and physical rehabilitation to restore the […]
Assessing head trauma in young children
New guidelines may help emergency department physicians reduce unnecessary scans in young children with minor head injuries, according to a new study. Researchers believe they have found two factors that would identify approximately 90 per cent of skull fractures in children under two months of age. This could reduce the number of radiographs by 60 […]
This is your brain on Whistled Turkish
While language is thought to be primarily a function of the brain’s left hemisphere, new research shows, it isn’t necessarily so. Whistled Turkish, a form of Turkish adapted into a series of whistles to allow for communication over greater distances, is processed equally in both brain hemispheres, researchers have found. Whistled Turkish is the only […]
Filming the brain activity of a fly
Using imaging technology together with technology for detecting neuronal activity from specific groups of cells, a team of researchers has been able to “film” the activity of the entire central nervous system of a developing fly, Drosophila melanogaster. This type of methodology is expected to help advance the understanding of the neuronal networks that dictate […]
Omega-3 may help to prevent psychotic disorders
Omega-3 may help reduce the risk of developing psychosis and psychiatric disorders, a study of 81 young people at high risk of developing schizophrenia shows. The participants were randomly split into two groups, one group received omega-3 daily for 12 weeks, while the other received a placebo. Seven years after the experiment, the researchers found […]
A possible explanation for visually vivid dreams during REM sleep
Researchers have found that during REM (rapid eye movement) sleep the human brain is responding in a way similar to visual processing during wakefulness. This may explain why individuals woken from REM sleep often report vivid dreams, and may reflect visual imagery during dreaming. The research team studied the activity of the medial temporal lobe […]
Healthy life, healthy mind
Healthy eating, exercising, and brain-training may be able to slow down cognitive decline in at risk individuals according to a new study. Researchers performed a randomised control trial of 1,260 people between 60 and 77 years old who were considered at risk for dementia. Individuals in the control group were given only regular health advice, […]
Use ’em or lose ’em – The case for teaching navigational skills
Schools should teach navigational and map reading skills to ensure future generations do not lose their innate ability to navigate in the world, so says Roger McKinlay, former president of the Royal Institute of Navigation in the United Kingdom. In this commentary, the author argues that turning to technology erodes our innate ability to orientate, […]