A new split-brain study reveals a clearer picture about the areas of the brain that play a role in complex reasoning, such as moral judgment. Historically, studying split-brain patients—those whose corpus callosum has been severed, effectively reducing communication between right and left hemispheres of the brain—has allowed researchers to gain greater insight into specific areas […]
Tag: brain

The brain chemistry of voles’ everlasting love
Voles are famous examples of social monogamy, a rare phenomenon in the animal kingdom. A recent study set to find out if there’s anything unique about these loving rodents’ brain connections that helps them form such strong bonds with their mate. Researchers specifically focused on the corticostriatal circuit in the brain, which is known to control the animals’ […]
Brain cells get to choose which parents’ genes to use
Researchers have long thought that most human cells express genes from both parents’ chromosomes equally throughout life. But as it turns out, when it comes to neurons, things aren’t so simple. A new study shows that it’s not unusual for individual neurons to choose to activate genes from one parent or the other. In particular, […]
Visualizing the blood-brain barrier
Using a microscope to see inside living tissue, researchers have found how the parasite Toxoplasma gondii passes through the blood brain barrier to invade the central nervous system. The researchers hope this finding will help develop effective strategies to stop the parasite from entering and damaging the brain. T. gondii infects about 30 per cent of […]
Genetically mapping the cause for schizophrenia’s synaptic loss
Mapping genetic variations has allowed researchers to identify a potential mechanism to explain the onset of schizophrenia. The authors hope this will provide insights into the risk of developing schizophrenia as well as the neurobiology of the disease. Variations in the genetic code controlling the production of C4, a protein known for the role it […]
Language changes brain patterns
Very early language experience will influence how a child’s brain processes a new language later in life, according to a study in Nature. Researchers examined three groups of children, all of whom were fluent in French. One group had no exposure to Mandarin, another was fluent in Mandarin, and the last third group had been […]
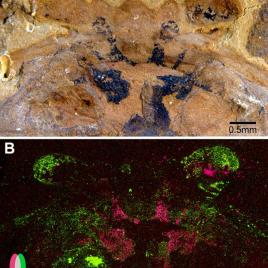
Proving paleontology wrong
Researchers have found what they believe is definitive evidence that brains do fossilize. In 2012 Nicholas Strausfeld co-authored the first ever report of a fossilized brain in an edition of Nature, however the findings were widely doubted as only one sample was found. Strausfeld and his team have now found seven fossil of the same […]
Brain cancer cells form connected network
Microtubes connecting brain tumor cells allow a specific type of brain cancer, known as gliomas, to spread quickly and become resistant to radiation therapy, a new study shows. This knowledge will allow researchers to target for future treatment efforts. These microtubes allow cancerous cells to reach out and form connections, allowing them to grow as […]
This is your brain on Whistled Turkish
While language is thought to be primarily a function of the brain’s left hemisphere, new research shows, it isn’t necessarily so. Whistled Turkish, a form of Turkish adapted into a series of whistles to allow for communication over greater distances, is processed equally in both brain hemispheres, researchers have found. Whistled Turkish is the only […]
Omega-3 may help to prevent psychotic disorders
Omega-3 may help reduce the risk of developing psychosis and psychiatric disorders, a study of 81 young people at high risk of developing schizophrenia shows. The participants were randomly split into two groups, one group received omega-3 daily for 12 weeks, while the other received a placebo. Seven years after the experiment, the researchers found […]
A possible explanation for visually vivid dreams during REM sleep
Researchers have found that during REM (rapid eye movement) sleep the human brain is responding in a way similar to visual processing during wakefulness. This may explain why individuals woken from REM sleep often report vivid dreams, and may reflect visual imagery during dreaming. The research team studied the activity of the medial temporal lobe […]
Damaged tau is the main cause behind Alzheimer’s disease
The main cause of Alzheimer’s disease is a dysfunctional protein according to a study of over 3,600 post-mortem brains. It was previously unknown if damaged or dysfunctional protein known as tau or amyloid build-up was the main cause of Alzheimer’s disease. A research team behind the new study believes that tau is Alzheimer’s primary cause. […]
Quitting is good for the brain
People who quit smoking may reduce or halt the thinning of the brain’s cortex. A new study has found that the cortex of the brain, which plays a key role in memory, attention, thought and language, is known to thin with age and this feature is used as one of the biological markers for cognitive […]
For sleeping children, quality is more important than quantity
For young children, the quality of sleep may be more important than the duration of sleep when it comes it academic performance, according to a new study. The researchers found that a high percentage of time in bed spent sleeping influenced positively a child’s grades in math, English, and French as a second language, while […]
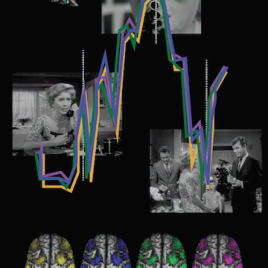
‘Vegetative’ patient follows the plot of an Hitchcock movie
Some patients thought to be in a vegetative state can have conscious experiences similar to healthy people, a new study shows. Researchers used fMRI to record the brain activity of 2 brain-injured patients and 12 healthy participants while they watched a 8-minute clip of an Alfred Hitchcock movie. One of the brain-injured patients, a man […]
Gene variant reduces risk of Alzheimer’s disease
A new study shows that a particular gene variation is associated with a lower risk of developing Alzheimer’s and a delay in the onset of symptoms. The study analyzed the brains of 800 Quebecers and found that a variant of a gene carried by about a quarter of the population is associated with a 50% […]
