The assembly instructions for nearly 1,000 protein complexes shared by most kinds of animals have been revealed, offering a new tool for studying the causes of diseases like Alzheimer’s and different cancers. Proteins come together to form complexes, or molecular machines, which are responsible for certain functions in cells. The new research indicates that most […]
Tag: genetics
Low vitamin D levels associated with an increased risk of MS
Low vitamin D levels are associated with an increased risk of multiple sclerosis (MS) in European populations, however whether vitamin D can delay or prevent the onset of MS requires further investigation, according to researchers. The authors used data from the International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium study, which involves 14,498 people with multiple sclerosis and […]
Finding the function of over 150 mouse genes
The largest analysis of mouse genes to date has identified the function of 159 genes whose purpose was previously unknown. The researchers developed new statistical methods to analyse the 413 measurements and 320 genes from each mouse. The new data set is available to the scientific community as a reference resource, and provides a strategy […]
Small cell lung cancer occurs when two genes are switched off
Using whole-genome sequencing researchers found that small cell lung cancer (SCLC) occurs when both copies of two separate genes responsible for tumor suppression are switched off. The research team hopes this discovery will help the development of new treatments for SCLC, which usually results in patient-death within months. Researchers sequenced the genome of 110 tumor […]

Discovering the hidden secrets of the woolly mammoth genome
Complete genome sequencing of two woolly mammoth (Mammuthus primigenius) specimens that lived approximately 4,300 and 44,800 years ago has been completed by researchers. The younger specimen was a member of one of last surviving mammoth populations. The researchers concluded that the woolly mammoth experienced a temporary population decline before recovering. This resulted in a reduction […]
Scientists genetically modify human embryos
In a world first, scientists have reported editing the genomes of human embryos. Chinese researchers using ‘non-viable’ embryos which cannot result in a live birth in order to attempt to modify the gene responsible for a potentially fatal blood disorder called β-thalassaemia. They used a gene-editing technique known as CRISPR/Cas9 (pronounced ‘crisper’) which allows you to […]
Why are the Dutch so tall?
The Dutch are currently the tallest people on earth, but 200 years ago they were among the shortest. A new study tries to explain how the Dutch population has grown 20 cm in average height in less than two centuries. Researchers observed in the Netherlands that taller men and average height women had more children […]
Incidental findings: What would you want to know?
With next-generation individual genome sequencing for medical reasons comes the ethical issue of uncovering incidental findings about one’s health. Would you like your physician to tell you that you are at risk for Alzheimer’s disease? Responding to an online questionnaire, 1200 Canadians answered that they generally would agree to receive information about high-risk disease disorders […]
Oncologists weigh the pros and cons of gene-expression profiling
Should women diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer have chemotherapy? To help make that choice, some physicians recommend gene-expression profiling (GEP) tests to identify patients who may benefit from the treatment. Carrying the brand name Oncotype DX, this test analyzes the patterns of 21 different genes within the cancer cells to help predict how likely it […]

Deadly coral snake venom
Researchers now understand why coral snake venom is so deadly and this knowledge could help provide insight into the biology of human diseases and conditions. Unlike most snake venoms which kill by paralyzing their victims, the venom of the coral snake (Micrurus mipartitus) causes deadly seizures. Scientists have discovered the venom’s active ingredient is a […]
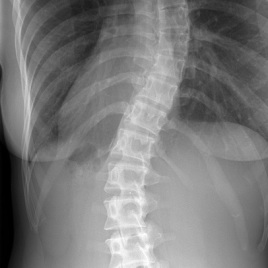
Gene causing common scoliosis identified
Researchers have identified the first gene causing idiopathic scoliosis, the most common type of spinal deformity. They identified 11 family members of a French family that were carriers of a rare variant of the gene, called POC5, and then used zebrafish to confirm that this variant really cause spinal deformity. This study is the first […]
How heritable is autism?
A new study shows how complex it is to understand autism from a genetic point of view. Researchers sequenced the genomes of 85 families with two children who are both affected with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). They found that the majority (around 70%) of affected siblings did not share common mutations. Greater than 100 susceptibility […]
Synthetic nutrients and GMOs
Researchers have developed genetically modified organisms (GMOs) that depend on synthetic nutrients to survive. Two teams, one from Yale University and another from Harvard, tweaked the genetic code of modified bacteria whose growth is restricted by the expression of multiple essential genes that depend on synthetic amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. When the […]
Language evolves faster in isolated populations
Changes in genetics and language follow similar patterns as human population disperse, however language is able to spontaneously change in isolated populations. Both genetics and language change over time as small mutations in genes or phonemes, like the ‘k’ sound in ‘cat’ or ‘skill’, accumulate or are lost. Additionally both language and genetics change by […]
Rare shared genetic mutation behind Inuit disease
Scientists have found the gene mutations responsible for a rare disease which impairs the function of the liver and muscles in about 1 in 2500 Inuits in northern Quebec. Called glycogen storage disease type IIIa, this sickness causes a buildup of glycogen, a complex sugar, in the body. This in turn produces low blood sugar […]
A new kind of stem cell
Scientists have observed a new class of stem cell with the capacity to turn into nearly any cell type. Called F-class cells for the fuzzy appearance of its colonies, these cells could potentially be used in regenerative medicine and drug discovery. In a second related paper, researchers with the Project Grandiose Consortium announce a new […]