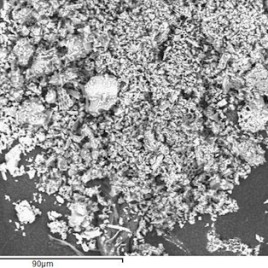
An experiment has shown that microscopic fossils can survive being fired from a gun and impacting at pressures up to 19 gigapascals (GPa). The fossils recovered by the researchers were smaller as projectile speed increased, however intact fossils were recovered from all trials. Researchers made the discovery by using fossilized diatoms – aquatic microorganisms with silica-based shells – […]
Take two parasites and call me in the morning
Two recent papers published by members of the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR) have questioned our traditional perception of intestinal parasites. The first, published July 14, 2014 in Trends in Parasitology is a systematic review of cases where humans have deliberately ingested parasites for research and suggests that certain parasites could have beneficial effects on conditions […]
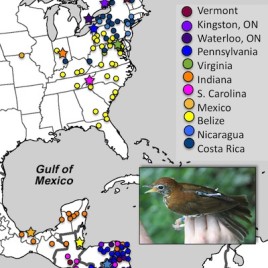
Wood thrushes ‘leap-frog’ during migration
Researchers have published the first detailed migratory map for different populations of wood thrushes. Over 100 birds were tracked using geolocators, a kind of ‘bird backpack’ that records sunrise and sunset times. Among other things, researchers found that the birds which travelled furthest north in the summer are also the ones that travel furthest south […]

Site of artefacts under threat
A new paper documents the rich density of artifacts found in the Kathu Townlands site in the Northern Cape province of South Africa. The site is dominated by a type of rock called chert that is ideal for making hand axes, small blades and other stone tools, and shows abundant evidence of having been […]

Des singes affectés par les radiations de Fukushima
Des singes sauvages japonais vivant dans une forêt à 70 km de la centrale nucléaire de Fukushima ont un nombre réduit de globules blancs et rouges révèlent une nouvelle étude. Les auteurs ont aussi remarqué que les niveaux de césium radioactif dans les muscles des singes étaient liés à la contamination des sols dans leur […]
Des oiseaux hybrides migrent de manière hybride
Une nouvelle étude montre que la génétique joue un rôle important dans les trajets migratoires choisis par les oiseaux. Des chercheurs ont attaché des petits sacs à dos de géolocalisation sur le dos de grives à dos olive afin de les suivre dans leur migration de la Colombie-Britannique jusqu’en Amérique centrale et du Sud. Les […]

L’expansion de la glace marine en Antarctique a été surestimée
Une nouvelle étude révèle que l’expansion observée de la glace marine en Antarctique serait due à une erreur dans la manière de traiter les données satellites. Dans les faits, la glace marine serait bien en train de fondre. Des chercheurs ont comparé les bases de données actuelles avec celles des années précédentes et ont remarqué […]

Les petites populations peuvent être plus diversifiées que prévu
Une nouvelle étude menée sur des ombles de fontaine vivant dans de petits ruisseaux montre que certaines populations sont assez génétiquement diversifiées pour être capables de s’adapter à des changements environnementaux futurs. Des populations d’ombles fontaines distinctes vivent dans chaque ruisseau du cap Race à Terre-Neuve depuis la dernière glaciation il y a 12 000 […]
Des bactéries dans le sperme seraient liées à la transmission du VIH
Une nouvelle étude montre que le nombre et la diversité de bactéries dans le sperme pourraient être liés à la concentration de VIH dans le sperme et pourrait donc avoir une connexion avec le risque de transmission. Bien que les bactéries soient communes dans le sperme, l’étude montre que le sperme d’hommes ayant des relations […]
Les anticoagulants ne sont pas utiles chez les femmes enceintes
Une nouvelle étude montre que les femmes enceintes à risque de développer des caillots sanguins qui s’injectent des anticoagulants ne réduisent pas les risques de complication de grossesse. Les médecins prescrivent de manière courante des anticoagulants chez les femmes enceintes à risque, représentant environ 10% d’entre elles, depuis les années 1990. Toutefois, aucun essai […]
Common blood thinner ineffective for pregnant women
A new study indicates that daily injections of a blood thinner does not effectively decrease the risk of pregnancy complications in women with a tendency to develop blood clots. A large-scale, randomized trial was never conducted and until now it’s effectiveness has been unknown. The new study followed 292 women over 12 years and […]
Bacteria present in semen linked to HIV transmission
A new study has found that the diversity and number of bacteria in semen are connected with the level of HIV virus and thus the risk of transmission. While bacteria are common in semen, the study found that HIV-infected men who have sex with men have lower bacterial diversity than uninfected controls. They also found […]

Small populations have more diversity than previously thought
Populations of trout living in streams with a small number of breeding adults still have enough genetic variation to be able to adapt to environmental changes according to a new study. Researchers found that streams with as few as 70 adults had more genetic variation than expected. Such variation provides a greater ability to adapt to environmental changes. […]

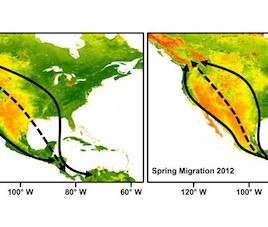
Mixed genes lead to mixed migration
A new study indicates that genetics can have a strong influence on bird migration patterns. Using geolocators strapped to the backs of Swainson’s thrushes researchers were able to map the birds’ migration from British Columbia to South and Central America each year. As expected birds of one population chose one route, while birds of another population chose another. However hybrid […]

Overestimation of Antarctic sea ice expansion
A new study says that the measured expansion of sea ice in the Antarctic may be due to an error in the way satellite data is processed as recent observations show the ice is actually retreating. Comparing past and present datasets revealed a difference between the two records. The current data shows much faster sea ice expansion […]

Blood changes in monkeys near Fukushima
Wild Japanese monkeys inhabiting a forest located 70 km from the Fukushima nuclear power plant have lower blood cell counts than monkeys from Northern Japan, a new study finds. The Fukushima nuclear power plant was badly damaged by a tsunami in March 2011. Red and white blood cell count were lower in the Fukushima monkeys. […]