It’s long been assumed that stone-tipped spears – the earliest examples of which appeared about 500,000 years ago – were a technological advance, but a new paper actually puts this theory to the test. Researchers used a cross-bow to fire wooden-tipped and stone-tipped spears into blocks of ballistics-grade gelatin. While both penetrated to a similar […]
Tag: evolution
A fish out of water . . . can get used to it
A new study shows just how much a fish can change when raised in a land environment, and sheds light on the role such changes could have played in the evolution of land animals. Bichir (Polypterus senegalus) have both gills and lungs and, although they prefer water, can walk across land to reach new habitat […]

Newfoundland fossil may be world’s oldest muscle
A 560 million-year-old fossil from Newoundland’s Bonavista Peninsula may record the oldest evidence of muscle tissue, according to a new paper. The fossil comes from a time known as the Ediacaran period, renowned for its preservation of the first large and complex organisms known. Most Ediacaran organisms were flat, sheet-like, or frond-like creatures whose […]

Ancient tuberculosis may have come from seals
Tuberculosis was already present in the Americas before European contact, and new research indicates that some strains may have arrived via an unusual route; seals and sea lions. Researchers have now sequenced the genomes of three strains of tuberculosis from 1000-year-old mummies from Peru. The strains are genetically very different from the European strains that […]
Genetically-modified salmon reproduce as fast as wild-type
Growth hormone (GH) transgenic salmon doesn’t reproduce faster than wild-type salmon, but transgenic salmon can reproduce with wild-type fish, a new study shows. GH transgenic salmon contains a chinook salmon growth hormone gene fused to an ocean pout antifreeze gene which significantly accelerate its growth rates. Researchers reared salmon in large (350,000 L), semi-natural, seawater tanks […]
Researchers shed (X-ray) light on how cystic fibrosis causes lung damage
Researchers are now able to directly visualize, for the first time, how the ability of airways to deal with inhaled bacteria is impaired in cystic fibrosis (CF) thanks to a new technique. Previous research has suggested that CF – which is caused by a mutation in the gene for a protein called CFTR – prevents […]
Lighting the way for more tomatoes
Researchers have found a gene in a wild species of tomato that allows the plant to tolerate continuous light, potentially leading to a 20% yield increase in commercial varieties. One of the major limitations for crop productivity is the amount of light available each day but cultivated tomato plants often develop damaging leaf injuries when […]

‘Hobbit’ Homo floriensis may not be a new species
The newly discovered ‘hobbit’-sized Homo floriensis found in Indonesia may only have been regular individual with Down syndrome, a new study suggests. A team of researchers shows in a first paper that the asymmetry of the skull and its small brain can be explained by some genetic disorder, and that it doesn’t provide enough evidence […]

Deep-sea octopus broods eggs for over 4 years
A new study documents the case of a deep-sea octopus who tended her eggs for nearly 4.5 years, by far the longest egg-brooding period ever reported for any animal species. The octopus was first spotted a remote controlled underwater in a submarine canyon of the coast of California in 2007. Researchers returned regularly until the eggs […]
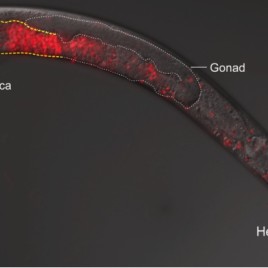
‘Killer sperm’ prevents mating between worm species
In Caenorhabditis worms, sperm from a foreign species can attack the organs of a female, rendering her sterile or even killing her according to new research. Researchers believe the ‘killer sperm’ may be the result of a divergence in the evolution of worm species’ sexual organs. For example, hermaphrodite worms—which produce their own sperm and fertilize […]

Small populations have more diversity than previously thought
Populations of trout living in streams with a small number of breeding adults still have enough genetic variation to be able to adapt to environmental changes according to a new study. Researchers found that streams with as few as 70 adults had more genetic variation than expected. Such variation provides a greater ability to adapt to environmental changes. […]
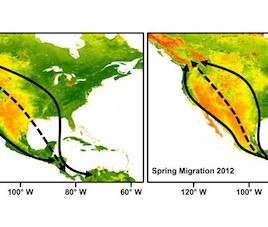
Mixed genes lead to mixed migration
A new study indicates that genetics can have a strong influence on bird migration patterns. Using geolocators strapped to the backs of Swainson’s thrushes researchers were able to map the birds’ migration from British Columbia to South and Central America each year. As expected birds of one population chose one route, while birds of another population chose another. However hybrid […]

Blood changes in monkeys near Fukushima
Wild Japanese monkeys inhabiting a forest located 70 km from the Fukushima nuclear power plant have lower blood cell counts than monkeys from Northern Japan, a new study finds. The Fukushima nuclear power plant was badly damaged by a tsunami in March 2011. Red and white blood cell count were lower in the Fukushima monkeys. […]

Moose spit de-toxifies plants
Moose and reindeer saliva may inhibit the growth of a toxic fungus that lives inside the grass known as red fescue. The researchers collected saliva from moose and reindeer from Canadian zoos, then applied it to grass that contained the toxic fungus. Their results showed that fungus grew more slowly and in some cases produced […]

Spotted green pigeon was a unique species
DNA analysis has shed light on the origins of the mysterious spotted green pigeon, of which only one stuffed specimen remains. The specimen is held by the World Museum in Liverpool UK, but there is no record of where the pigeon was found, nor are there any records of sightings in the wild. DNA barcoding […]

Ancient creatures display modern features
New, well-preserved fossils from China suggest that an ancient sea predator may share nervous system features with its modern descendants. Anomalocaridids are creatures from the Cambrian era – over 500 million years ago – first described from fossils found in the Burgess Shale, in British Columbia’s Yoho National Park. The new fossils from China describe […]
