Monarch butterflies originated in North America 20,000 years ago at the end of the last glacial maximum before dispersing out to locations around the world, a new study shows. The authors sequenced the whole genome of 101 monarch butterflies from around the world to better understand the genetic basis of its migration patterns. The researchers […]
Tag: biology

The highs and lows of marijuana use
A new study helps explain why the same drug can have opposite effects at different doses. Using a drug that binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain – the same ones that are activated by cannabis – researchers showed the precise pathway by which low doses stimulate the brain’s dopamine system, which can lead to […]

David vs. Goliath: How small birds compete
One might think that larger birds invariably win fights with smaller ones, but a new study explains why that is not always the case. Researchers studied vultures at carcasses, hummingbirds at nectar sources, as well as antbirds and woodcreepers at army ant swarms to discover that some small birds have evolved ways to beat their opponents. […]
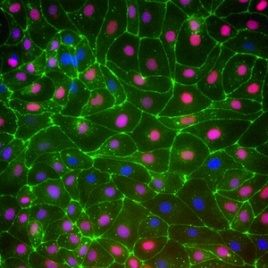
Lab-grown cells could help combat heart diseases
For the first time, researchers have grown a type of heart cell called an epicardial cell from stem cells in the lab, an accomplishment that could help in developing new treatments for heart disease. Epciardial cells form a protective membrane around the adult heart, and during fetal life provide a source of specialized structural cells […]
A fish out of water . . . can get used to it
A new study shows just how much a fish can change when raised in a land environment, and sheds light on the role such changes could have played in the evolution of land animals. Bichir (Polypterus senegalus) have both gills and lungs and, although they prefer water, can walk across land to reach new habitat […]

Newfoundland fossil may be world’s oldest muscle
A 560 million-year-old fossil from Newoundland’s Bonavista Peninsula may record the oldest evidence of muscle tissue, according to a new paper. The fossil comes from a time known as the Ediacaran period, renowned for its preservation of the first large and complex organisms known. Most Ediacaran organisms were flat, sheet-like, or frond-like creatures whose […]

Ancient tuberculosis may have come from seals
Tuberculosis was already present in the Americas before European contact, and new research indicates that some strains may have arrived via an unusual route; seals and sea lions. Researchers have now sequenced the genomes of three strains of tuberculosis from 1000-year-old mummies from Peru. The strains are genetically very different from the European strains that […]

Deep-sea octopus broods eggs for over 4 years
A new study documents the case of a deep-sea octopus who tended her eggs for nearly 4.5 years, by far the longest egg-brooding period ever reported for any animal species. The octopus was first spotted a remote controlled underwater in a submarine canyon of the coast of California in 2007. Researchers returned regularly until the eggs […]
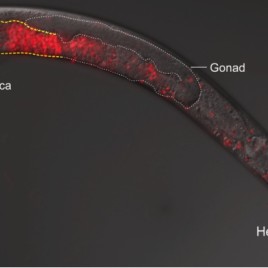
‘Killer sperm’ prevents mating between worm species
In Caenorhabditis worms, sperm from a foreign species can attack the organs of a female, rendering her sterile or even killing her according to new research. Researchers believe the ‘killer sperm’ may be the result of a divergence in the evolution of worm species’ sexual organs. For example, hermaphrodite worms—which produce their own sperm and fertilize […]

Small populations have more diversity than previously thought
Populations of trout living in streams with a small number of breeding adults still have enough genetic variation to be able to adapt to environmental changes according to a new study. Researchers found that streams with as few as 70 adults had more genetic variation than expected. Such variation provides a greater ability to adapt to environmental changes. […]
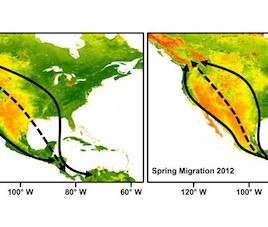
Mixed genes lead to mixed migration
A new study indicates that genetics can have a strong influence on bird migration patterns. Using geolocators strapped to the backs of Swainson’s thrushes researchers were able to map the birds’ migration from British Columbia to South and Central America each year. As expected birds of one population chose one route, while birds of another population chose another. However hybrid […]

Blood changes in monkeys near Fukushima
Wild Japanese monkeys inhabiting a forest located 70 km from the Fukushima nuclear power plant have lower blood cell counts than monkeys from Northern Japan, a new study finds. The Fukushima nuclear power plant was badly damaged by a tsunami in March 2011. Red and white blood cell count were lower in the Fukushima monkeys. […]

Moose spit de-toxifies plants
Moose and reindeer saliva may inhibit the growth of a toxic fungus that lives inside the grass known as red fescue. The researchers collected saliva from moose and reindeer from Canadian zoos, then applied it to grass that contained the toxic fungus. Their results showed that fungus grew more slowly and in some cases produced […]

Caribous and wolves metabolize some pesticides
Caribou and wolves living in the Canadian Arctic are able to metabolize some pesticides according to a new study. By analyzing local vegetation and the tissue of captured caribous and wolves researchers looked to see if the pesticide levels would biomagnify – increase in concentration up the food chain. They saw that while currently used pesticides do enter the food […]

The 1000 Bulls Project: New bovine genomes published
The first phase of the “1000 Bulls Project” reports complete DNA sequences for 234 animals that are considered key ancestors of the worldwide Holstein-Fresian, Jersey and Fleckvieh breeds. By cross-referencing the tiny differences in these genomes with information on the animals performance – milk production (in dairy animals), weight gain (in beef cattle), genetic defects, […]

Palm oil agriculture could means trouble for Africa’s great apes
The booming oil palm industry in West and Central Africa could have a negative impact on great apes, a new study shows. The authors estimate that nearly 40% of the distribution of great ape species on unprotected lands overlaps with suitable oil palm areas. The countries most at risk are Gabon, Congo, and The Democratic […]
