Scientists have decoded the genome of Brassica napus, the plant that gives us canola oil. Developed in the 1970s by researchers from the University of Manitoba, Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC), and National Research Council (NRC) in Saskatoon (“canola” stands for CANadian Oil Low Acid) the crop has gained huge commercial importance. Because Brassica napus […]
MERS-CoV: Marmosets get sick like humans
Researchers have found that marmosets could be used as an animal model to study the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus, also known as MERS-CoV. They observed that marmosets carry the same variant of a cell surface protein (DPP4) that MERS-CoV uses to invade human cells. This means that marmosets infected by MERS-CoV get as sick […]

Ancient tuberculosis may have come from seals
Tuberculosis was already present in the Americas before European contact, and new research indicates that some strains may have arrived via an unusual route; seals and sea lions. Researchers have now sequenced the genomes of three strains of tuberculosis from 1000-year-old mummies from Peru. The strains are genetically very different from the European strains that […]
Genetically-modified salmon reproduce as fast as wild-type
Growth hormone (GH) transgenic salmon doesn’t reproduce faster than wild-type salmon, but transgenic salmon can reproduce with wild-type fish, a new study shows. GH transgenic salmon contains a chinook salmon growth hormone gene fused to an ocean pout antifreeze gene which significantly accelerate its growth rates. Researchers reared salmon in large (350,000 L), semi-natural, seawater tanks […]

Iceland Bardarbunga volcano at an increased risk of eruption
Four years after ash from the Eyjafjallajokull volcano in Iceland disrupted air traffic in Europe for six days, scientists have heard ominous rumblings from another volcano, Bardarbunga. On August 18, the Icelandic Meteorological Office raised aviation alert level to orange, meaning that “it shows heightened or escalating unrest with increased potential of eruption”. Intense seismic […]

First flight: why young birds migrate more slowly
A slower migration from overwintering grounds in Belize and Costa Rica to breeding grounds in Canada may help young wood thrushes avoid competition with adults, a new study shows. Using data from geolocators – a kind of bird backpack that records location information – researchers showed that juvenile birds leave almost 2 weeks behind the […]

Une précaution supplémentaire avant de recommander
La Société canadienne de physiologie de l’exercice demande aux professionnels de la santé de vérifier les antécédents médicaux d’un enfant avant de lui recommander de faire de l’exercice physique. Les chercheurs maintiennent la balise que tout enfant devrait faire de l’activité physique pendant au moins 60 minutes, 3 fois par semaine. Ces nouvelles recommandations visent […]

Taking extra precaution before recommending physical activity to children
New recommendations from the Canadian Society for Exercise Physiology state that physicians should promote physical activity to children, but not before checking whether the child has underlying medical conditions or is sedentary. Researchers maintain that children should exercise for at least 60 minutes, 3 times a week. The new guidelines advise checking for previous medical […]
How gut bacteria train our immune system
A new study helps shed light on which beneficial bacteria are needed to help train our immune system. Newborn mice were treated with vancomycin or streptomycin, two antibiotics that each kill certain species of gut bacteria but leave others relatively unaffected. Those treated with streptomycin were much more likely to develop a lung condition that […]

Le braconnage accélère le déclin des éléphants africains
Des chercheurs estiment que le braconnage est responsable de 7% de tous les décès d’éléphants en Afique entre 2010 et 2012. Les auteurs ont commencé par recenser les carcasses d’éléphants dans la réserve de Samburu au Kenya afin d’estimer les causes de décès. Ils ont ensuite construit un modèle pour estimer le taux de braconnage […]

Poaching drives decline in African elephants
Researchers estimate that 7% of all elephants deaths in Africa between 2010 and 2012 can be attributed to illegal killings. The authors first surveyed elephant carcasses in Kenya’s Samburu National Reserve to distinguish between illegal and natural causes of mortality, then built a model to estimate poaching on the continent. The authors conclude that […]
Un rayon X de comment la fibrose kystique attaque les poumons
Des chercheurs peuvent maintenant voir en temps réel comment la fibrose kystique attaque les poumons et les empêchent de combattre certaines bactéries. Cela est rendu possible grâce à une nouvelle technique qui utilise des rayons X ultralumineux provenant du Centre canadien de rayonnement synchrotron pour irradier la trachée de porcs. Les chercheurs ont pu ainsi […]
Researchers shed (X-ray) light on how cystic fibrosis causes lung damage
Researchers are now able to directly visualize, for the first time, how the ability of airways to deal with inhaled bacteria is impaired in cystic fibrosis (CF) thanks to a new technique. Previous research has suggested that CF – which is caused by a mutation in the gene for a protein called CFTR – prevents […]

Des arbres qui empiètent sur les vaches
Quand les prairies et les savanes se transforment en forêt, les populations de bétail comme les vaches laitières et les boeufs diminuent selon une nouvelle étude. À l’aide d’une simulation informatique, les auteurs montrent qu’une augmentation de 1% du couvert forestier correspond à une baisse de 2% du nombre moyen de vaches par kilomètre carré. […]

Are trees crowding out cows?
Livestock like beef cows can suffer when grasslands, shrublands and savannas shift to a more tree-covered landscape and new research has put a number on this effect. Using computer models the authors show that for every 1 per cent increase in tree cover, the number of reproductive cows per square kilometre drops by about 2 […]
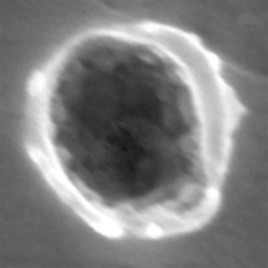
Citizen scientists help find pieces of deep space stardust
Particles discovered by volunteers sifting through photos from NASA’s Stardust spacecraft are very likely dust from the vast space between stars, according to a new paper. The particles were collected by exposing a soft absorbent material called an aerogel to the vastness of space. When the spacecraft returned to earth, the aerogel was photographed under […]
