Les chercheurs ont passé au crible des médicaments afin de déterminer leur capacité à prévenir la croissance de bactéries dangereuses. La plupart des antibiotiques interfèrent avec le ribosome des bactéries, l’organelle responsable de la production de protéines et d’enzymes essentielles à la survie de la bactérie. Les chercheurs ont concentré leurs efforts afin de trouver […]
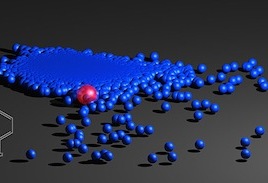
Old drug may be key to new antibiotics
Researchers screening old drugs for new uses have found one that offers a previously untapped strategy for preventing the growth of harmful bacteria. Many antibiotics work by interfering with the bacterial ribosome, a kind of biochemical workshop where proteins and enzymes needed for the growth of the bacterium are produced. In this case, the team […]
Les personnes d’origine sud-asiatique ont un plus grand risque de maladies cardiovasculaires
Une nouvelle revue de littérature révèle que les Canadiens d’origine sud-asiatique ont un plus grand risque de développer des maladies cardiovasculaires et du diabète que les Canadiens blancs. Toutefois, ils fument moins et sont moins obèses. Plus d’un million de Canadiens sont nés en Inde, au Pakistan, au Sri Lanka, au Népal ou au Bengandlesh, […]
South Asians in Canada have higher risk of heart disease
Canadians of South Asian background are more at risk of heart disease and diabetes than white Canadians, a new review of literature reports. However, they are less likely to smoke and are less obese. More than one million Canadians whose ethnicity hails from India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Nepal and Bangladesh live in Canada, comprising about […]

Comment le canyon Fraser reste escarpé
Une nouvelle étude révèle la dynamique de la rivière qui creuse le canyon Fraser long de 542 kilomètres en Colombie-Britannique et explique comment les parois du canyon restent escarpées. Les chercheurs ont utilisé un dispositif sonore monté sur un radeau afin d’analyser la vitesse du flot de l’eau à différentes profondeurs et à divers endroits […]
De l’eau trouvée sur une exoplanète de taille similaire à Neptune
Des astronomes ont détecté de la vapeur d’eau dans l’atmosphère d’une exoplanète de taille similaire à Neptune. Auparavant, de l’eau avait été seulement détectée sur des exoplanètes plus grosses, de la taille de Jupiter. Les auteurs ont utilisé une technique appelée la spectroscopie par transmission avec laquelle ils ont analysé le spectre de lumière provenant […]
Water found on Neptune-sized exoplanet
Astronomers have detected water vapour in the atmosphere of Neptune-sized exoplanet. Previously, it had only been possible to measure the atmospheric composition in large, Jupiter-sized exoplanets. Using a technique called transmission spectroscopy with which they analysed the light spectrum coming from the exoplanet, they’ve detected water molecules in the atmosphere of HAT-P-11b, an exoplanet with […]

‘Upside-down’ water flows keep the Fraser Canyon steep
A new study shows water in certain stretches of the 542-kilometre Fraser Canyon in British Columbia is flowing ‘upside-down’, a discovery that helps explain why the canyon walls remain so steep. Researchers discovered that high velocity water flows down into deep pools and then upwells along the canyon walls, such that the water along the bottom flowing […]

How will climate change affect sugar maples?
A changing climate means trees will grow in new places, but an experiment with sugar maples shows that other factors – such as soil conditions or seed predation – need to be taken into account as well. Researchers grew maple seedlings on the slopes of a Quebec mountain where climate conditions are more favourable for […]

22 new strategies for improving child/maternal health in the developing world
Federally-funded Grand Challenges Canada announced seed funding Sept. 22 for 22 projects submitted by innovators worldwide and designed to improve child and maternal health in the developing world. Examples include: A snack produced from rice bran waste in the Philippines to combat child iron deficiency; A technique for safely storing vaccines at room temperature by […]
Carbon quotas are nearly used up
Two upcoming papers discuss the concept of a carbon quota, that is, a limited amount of carbon that can be released to the atmosphere in order to remain below a certain global warming target. The first paper, published in Nature Geoscience, indicates that we have already used up two thirds of the carbon quota needed […]
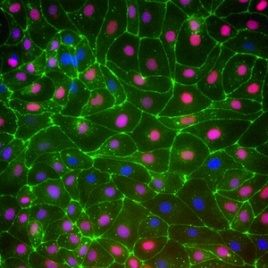
Lab-grown cells could help combat heart diseases
For the first time, researchers have grown a type of heart cell called an epicardial cell from stem cells in the lab, an accomplishment that could help in developing new treatments for heart disease. Epciardial cells form a protective membrane around the adult heart, and during fetal life provide a source of specialized structural cells […]

Microplastic pollution found in the St. Lawrence River
Concentrations of microplastic particles in the St. Lawrence are as high as has been observed in the world’s most contaminated marine sediments, a new study shows. This is also the first time such pollutants have been found in freshwater sediments. The authors dug up microplastics (in the form of polyethylene ‘microbeads’, <2 mm diameter) from the […]
Chemicals could help bee colonies fight mite infestations
Researchers have identified certain chemical compounds that could help fight infestations of the parasitic Varroa destructor mite, a major pest for beekeepers. The mites use smell to distinguish between different worker types in the bee colony, preferring younger ‘nurse’ bees over older foragers. The team found that treating the bees with certain chemical compounds confused […]
World Alzheimer Report 2014 – What’s good for your heart is good for your brain
Control of diabetes and high blood pressure as well as smoking cessation have the potential to reduce the risk of dementia even in late-life, a new report says. Looking at the literature, they report for example that diabetes can increase the risk of dementia by 50%. The report also includes survey data which shows […]
Climate change: cropland could expand in Canada
A new simulation of the impact of climate change on the supply of agricultural land shows that suitable cropland will expand in Canada, Russia, China and other countries in the high latitudes of the Northern hemisphere. On the other hand the authors project a significant loss of highly fertile cropland in the Mediterranean regions and […]